How to Upload a Png File to Krita
Working with Images¶
Computers piece of work with files and as a painting plan, Krita works with images as the type of file it creates and manipulates.
What do Images Comprise?¶
If you have a text document, information technology of course contains letters, strung in the correct society, so the reckoner loads them as coherent sentences.
Raster Data¶
This is the master information on the pigment layers yous make. And so these are the strokes with the paint brush and expect pixelated upwards close. A multi-layer file will incorporate several of such layers, that become overlaid on elevation of each other and so make the concluding image.
A single layer file will usually just contain raster data.
Vector Information¶
These are mathematical operations that tell the reckoner to draw pixels on a spot. This makes them much more scalable, because you lot just tell the operation to make the coordinates iv times bigger to calibration it upwards. Due to this vector information is much more editable, lighter, but at the same time it's also much more CPU intensive.
Performance Information¶
Stuff like the filter layers, that tells Krita to change the colors of a layer, only also transparency masks, group layer and transformation masks are saved to multi-layer files. Being able to load these depend on the software that initially made the file. So Krita can load and salvage groups, transparency masks and layer furnishings from PSD, simply non load or relieve transform masks.
Metadata¶
Metadata is information similar the creation date, author, description and also data like DPI.
Epitome size¶
The image size is the dimension and resolution of the canvas. Image size has direct event file size of the Krita certificate. The more pixels that need to be remembered and the college the bit depth of the color, the heavier the resulting file will be.
DPI/PPI¶
DPI stands for Dots per Inch, PPI stands for Pixels per Inch. In printing industry, suppose if your printer prints at 300 DPI . Information technology means it is actually putting 300 dots of colors in an area equal to an Inch. This ways the number of pixels your artwork has in a relative area of an inch.
DPI is the concern of the printer, and artists while creating artwork should continue PPI in mind. According to the PPI you have set, the printers can make up one's mind how big your image should be on a piece of paper.
Some standards:
- 72 PPI
-
This is the default PPI of monitors as assumed past all programs. It is non fully correct, as about monitors these days take 125 PPI or even 300 PPI for the retina devices. Nonetheless, when making an image for computer consumption, this is the default.
- 120 PPI
-
This is oft used every bit a standard for low-quality posters.
- 300 PPI
-
This is the minimum you lot should use for quality prints.
- 600 PPI
-
The quality used for line art for comics.
Color depth¶
Nosotros went over color depth in the Color Management page. What you lot need to sympathize is that Krita has paradigm color spaces, and layer color spaces, the latter which can save memory if used correct. For example, having a line art layer in grayscale can half the memory costs.
Image color infinite vs layer color space vs conversion.¶
Because at that place's a divergence between image color space and layer color infinite, you can change just the image color space in which will leave the layers lone. But if yous want to change the color space of the file including all the layers you tin practise it by going to this will convert all the layers color space as well.
Cropping and resizing the sheet¶
You can crop and image with the Crop Tool, to cut abroad extra space and improve the composition.
Trimming¶
Using , Krita resizes the image to the dimensions of the layer selected. Useful for when you paste a too large image into the layer and want to resize the canvas to the extent of this layer.
is a faster cousin to the crop tool. This helps usa to resize the sheet to the dimension of whatever active selection. This is peculiarly useful with right-clicking the layer on the layer stack and choosing Select Opaque. will then crop the canvas to the selection bounding box.
is actually for layers, and will trim all layers to the size of the paradigm, making your files lighter by getting rid of invisible information.
Resizing the canvas¶
You can besides resize the canvas via (or the Ctrl + Alt + C shortcut). The dialog box is shown below.
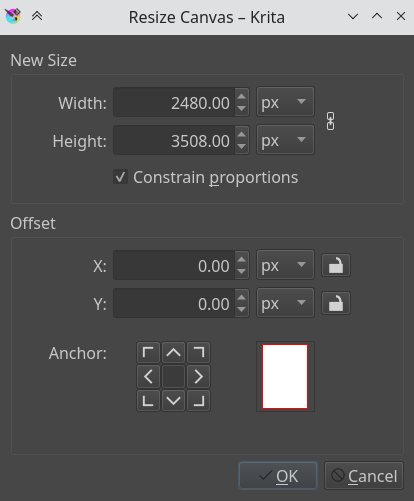
In this, Constrain proportions checkbox will brand sure the height and width stay in proportion to each other as yous alter them. Offset indicates where the new canvas space is added around the current epitome. Yous basically decide where the current image goes (if you press the left-push button, it'll go to the center left, and the new canvas space will be added to the correct of the image).
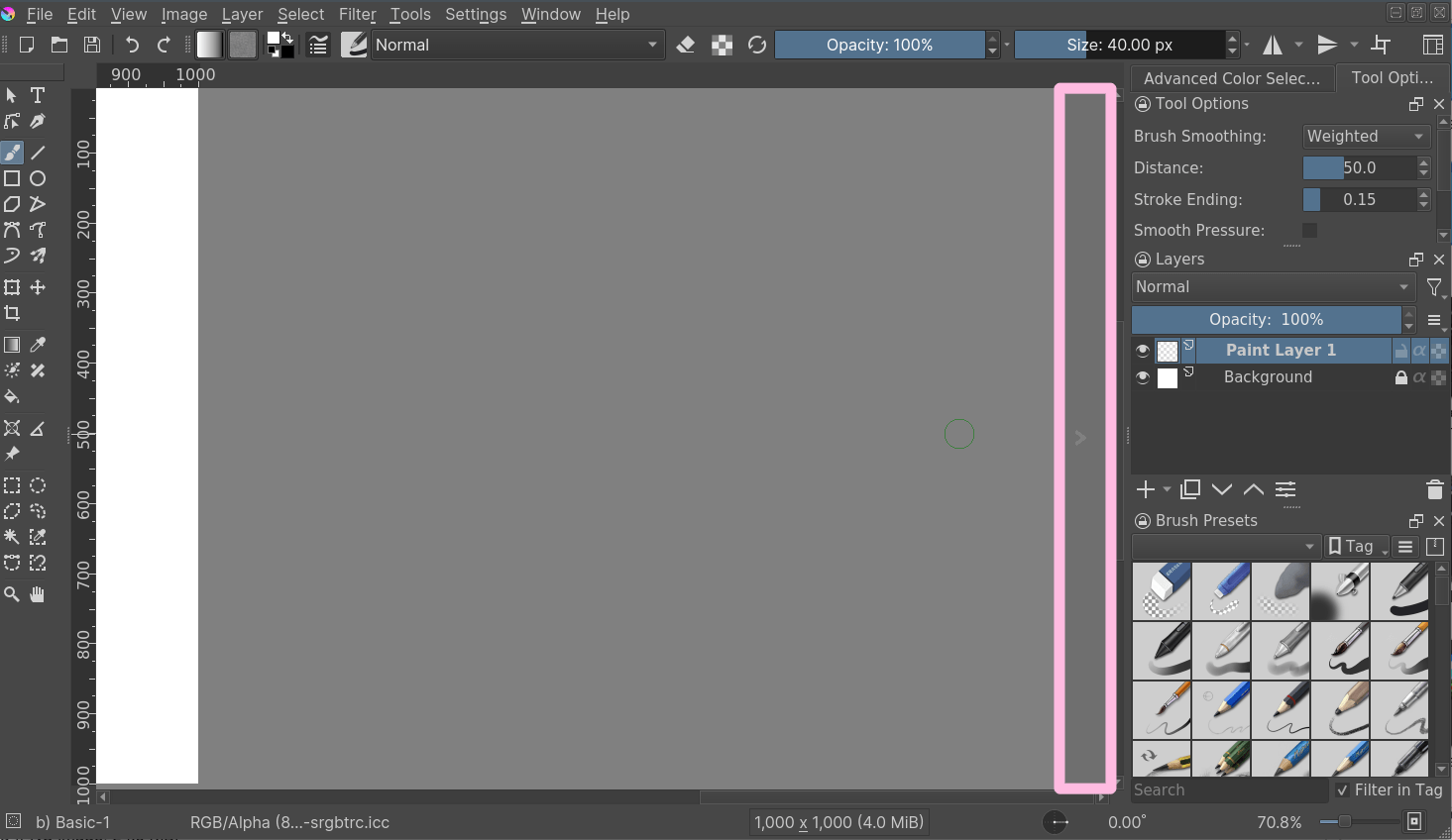
Another manner to resize the canvas according to the need while cartoon is when you scroll away from the end of the sail, you lot tin see a strip with an arrow appear. Clicking this will extend the sheet in that management. You lot tin can see the arrow marked in red in the example below:
Resizing the paradigm¶
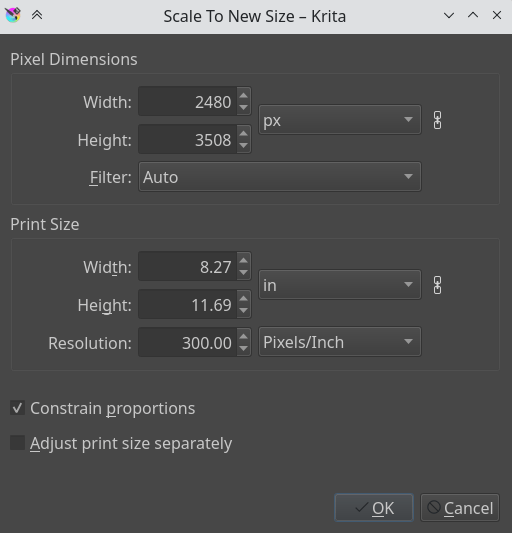
Scale Image to New Size… allows you to resize the whole prototype. Also, importantly, this is where you can alter the resolution or upres your prototype. And so for instance, if you were initially working at 72 PPI to block in large shapes and colors, images, etc… And now you want to really go in and practise some particular work at 300 or 400 PPI this is where you would make the change.
Like all other dialogs where a chain link appears, when the chain is linked the aspect ratio is maintained. To disconnect the chain, just click on the link and the 2 halves will split.
Separating Images¶
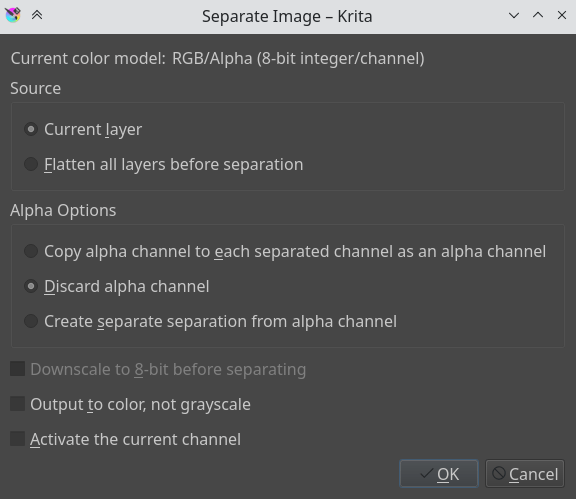
This powerful epitome manipulation characteristic lets you separate an image into its different components or channels.
This is useful for people working in print, or people manipulating game textures. In that location's no combine functionality, but what you can do, if using colored output, is to set two of the channels to the addition Blending Modes.
For grayscale images in the RGB infinite, you tin can use the Re-create Red, Re-create Dark-green and Copy Blue blending modes, with using the red one for the scarlet channel paradigm, etc.
Saving, Exporting and Opening Files¶
When Krita creates or opens a file, it has a copy of the file in memory, that it edits. This is function of the style how computers piece of work: They make a copy of their file in the RAM. Thus, when saving, Krita takes its re-create and copies information technology over the existing file. At that place'due south a couple of tricks you can do with saving.
- Relieve
-
Krita saves the electric current image in its retention to a defined identify on the hard-drive. If the image hadn't been saved before, Krita will ask you where to save it.
- Save As…
-
Brand a copy of your electric current file past saving it with a unlike name. Krita volition switch to the newly made file every bit its active certificate.
- Open up…
-
Open a saved file. Fairly straightforward.
- Export…
-
Save a file to a new location without actively opening it. Useful for when you are working on a layered file, but but need to save a flattened version of it to a sure location.
- Open Existing Document as Untitled Document…
-
This is a bit of an odd ane, but it opens a file, and forgets where y'all saved information technology to, so that when pressing 'save' information technology asks you where to save it. This is also called 'import' in other programs.
- Create Copy from Electric current Image
-
Makes a new copy of the electric current epitome. Similar to , but and then with already opened files.
- Relieve Incremental Version
-
Saves the current image as
filename_XXX.kraand switches the electric current document to it. - Save Incremental Backup
-
Copies and renames the last saved version of your file to a backup file and saves your certificate nether the original name.
Note
Since Krita'due south file format is compressed data file, in case of a corrupt or cleaved file y'all can open it with archive managers and extract the contents of the layers. This will assistance you lot to recover as much every bit possible information from the file. On Windows, y'all will need to rename information technology to filename.zip to open up it.
guerardsenclavoked.blogspot.com
Source: https://docs.krita.org/en/user_manual/working_with_images.html